Advantages of Blockchain
Category: About Blockchain
Tags: advantages, blockchain
-
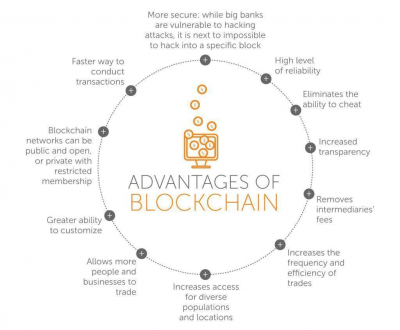
Description: Decentralization: One of the key advantages of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Traditional systems often rely on central authorities or intermediaries to validate and record transactions. In contrast, blockchain operates on a distributed network of nodes, where transactions are verified and recorded by multiple participants. This decentralization enhances security, as there is no single point of failure, and increases trust among network participants.
-
Transparency: Blockchain provides transparency through its open and immutable ledger. Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity of the data. This transparency fosters trust among users, as they can independently verify the history of transactions without relying on intermediaries.
-
Security: Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and data. Each block in the blockchain is linked to the previous one using cryptographic hashes, creating a tamper-evident record. Additionally, consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) ensure that transactions are validated and added to the blockchain in a secure and transparent manner.
-
Efficiency and Speed: Blockchain streamlines processes by eliminating intermediaries and automating tasks through smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded on the blockchain, which automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. This automation reduces the need for manual intervention, resulting in faster and more efficient transactions.
-
Cost Reduction: By removing intermediaries and streamlining processes, blockchain technology can significantly reduce transaction costs. Traditional financial transactions often involve fees associated with intermediaries such as banks, clearinghouses, or brokers. With blockchain, these fees can be minimized or eliminated, leading to cost savings for businesses and individuals.
-
Immutable Record-keeping: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from the network participants. This immutability ensures the integrity and reliability of the data, making blockchain an ideal solution for applications where tamper-proof record-keeping is essential, such as supply chain management, voting systems, and healthcare records.
-
Accessibility: Blockchain technology provides access to financial services and other applications to individuals who are underserved or excluded from traditional banking systems. With blockchain, anyone with internet access can participate in the network and access financial services, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status.
Loading...
