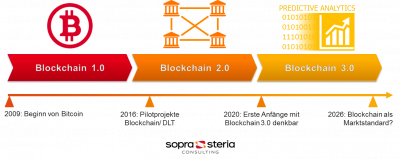
Blockchain Evolution 1.0 - 2.0 - 3.0
Category: About Blockchain
Tags: evolution, blockchain
Description: Blockchain evolution can be divided into distinct phases, often referred to as Blockchain 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0, each representing a significant advancement in technology and use cases:
-
Blockchain 1.0 - Bitcoin:
- Bitcoin, introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008, marked the beginning of blockchain technology.
- Blockchain 1.0 primarily focused on cryptocurrency and financial transactions, with Bitcoin serving as a decentralized digital currency.
- The key innovation of Blockchain 1.0 was the creation of a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger through the use of cryptographic techniques and decentralized consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW).
-
Blockchain 2.0 - Ethereum and Smart Contracts:
- Ethereum, launched in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin, represents the next phase of blockchain evolution by introducing smart contracts.
- Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They enable the automation of complex transactions and the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) on the blockchain.
- Ethereum's introduction of smart contracts expanded the utility of blockchain beyond simple peer-to-peer transactions, allowing for the development of decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
-
Blockchain 3.0 - Scalability, Interoperability, and Enterprise Adoption:
- Blockchain 3.0 aims to address the scalability and interoperability challenges faced by earlier blockchain platforms.
- Projects like Polkadot, Cosmos, and Cardano are working on solutions to enhance scalability, allowing blockchain networks to handle a larger number of transactions per second (TPS) without sacrificing security or decentralization.
- Interoperability protocols are being developed to enable seamless communication and data exchange between different blockchain networks, facilitating the integration of disparate systems and enhancing overall network efficiency.
- Enterprise adoption of blockchain technology is gaining traction in Blockchain 3.0, with companies exploring use cases beyond cryptocurrency, such as supply chain management, identity verification, and tokenization of assets.
- Future advancements in blockchain technology may include improvements in privacy, consensus mechanisms, sustainability, and governance, paving the way for broader adoption and real-world impact across various industries.
Loading...
